Soft Tissue Neck Radiographs - Are They Useful?
/In March 2015, Dr. Renne did a Grand Rounds lecture on soft tissue neck radiographs, which offers a great review of normal anatomy and systematic approach to reading films (“CHESS”). Yet, in my small, informal (not scientific at all) poll of some of our residents, none had ever ordered a soft tissue neck film. Are soft tissue neck radiographs useful? You be the judge.
Why order a soft tissue neck radiograph?
- Evidence of upper airway obstruction on exam
Why would I ever order an x-ray over CT?
- Quicker than CT
- Patient too unstable to go to CT
- Airway compromise if lying flat
- Decreased neck radiation, especially in children
- Cheap! (Something we probably don’t think enough about.)
What diagnostic entities can be inferred or seen on a soft tissue neck x-ray?
- Foreign body
- Retropharyngeal abscess
- Epiglottitis
- Croup
- Bacterial tracheitis
- Neck tumors (4T’s: thyroid, thymoma, teratoma, terrible lymphoma)
- Enlarged tonsils and/or adenoids (less ED, more outpatient)
Okay, I ordered the x-ray. Now what? What should I be looking for on the films?
See Dr. Renne’s previous blog post or below. As long as you’re systematic, you’ll be good!
PATIENT 1
A 30-month-old boy is brought in for barky cough and fever. On exam, patient has inspiratory stridor when crying but is otherwise well appearing.
Do we need an x-ray to confirm the diagnosis?
While steeple sign gets ingrained in our heads from standardized test taking, croup is a clinical diagnosis; an x-ray should not be ordered unless there is concern for other pathology. Steeple sign can be seen in normal children depending on the variation of respirations and in many other diagnoses (i.e. bacterial tracheitis, epiglottitis, thermal injury, angioneurotic edema) making it not specific to croup despite what we’ve been told.
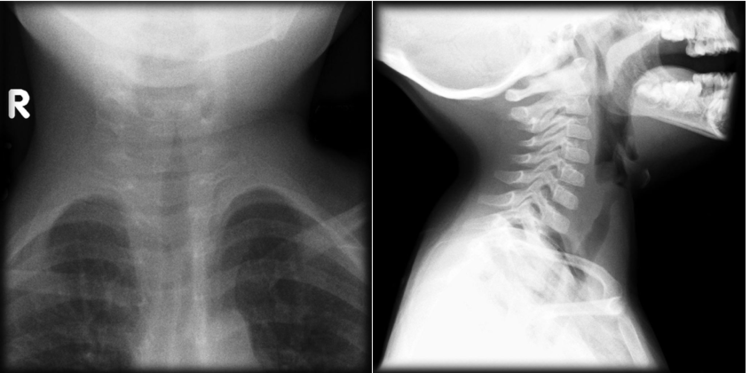
- Left - Subglottic Swelling "Steeple Sign"
- Right - Overdistension of the hypopharynx
- Case Courtesy of Dr. Michael Sargent, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 6086
PATIENT 2
A 6-year-old unvaccinated girl is brought in for fever and dysphagia. On exam, she appears toxic, is in severe respiratory distress, and has expiratory stridor.
What is the next step in the management of this patient?
Airway management. This patient has epiglottitis, another clinical diagnosis. Do not delay getting control of the patient’s airway in order to obtain diagnostic imaging, especially in such a clear-cut case. However, if there is any diagnostic uncertainty, the best initial and most useful test is a soft tissue neck x-ray with signs such as:


¡Cuidado!
X-ray is highly specific but not sensitive for epiglottitis. If you have a high clinical suspicion, a negative x-ray should not make you feel better. In a recent article, false negative rate was 31.9% with previous oral antibiotic use as an independent risk factor.
- [L] Thumbprint sign, vallecula sign, and epiglottis width > 6.3 mm
*Case courtesy of Dr. Andrew Ho, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 22906 (modified) - [R] Asterisk emphasizing normal vallecula airspace Case courtesy of Dr. Henry Knipe, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 46366 (modified) *
PATIENT 3
A 20-year-old female presents with dysphagia and foreign body sensation. On exam, patient is well appearing and in no respiratory distress.
Is the x-ray normal or abnormal?
Abnormal. There is an oval hypodensity at C6-7 with prevertebral swelling and loss of cervical lordosis consistent with a foreign body—in this case a plum pit. Most foreign bodies are organic and not directly visible, so be sure to look for indirect signs including: foreign body shadow, esophageal air, loss of cervical lordosis, prevertebral swelling, or soft tissue emphysema. The level of the cricopharyngeus muscle, C6-7, is the most common location for bone and food bolus impactions.

Board Review Tip! On frOntal view, a FB in cOronal plane is located in the esOphagus
Clinical Pro Tip! If parents bring in what they think the child may have swallowed, such as a bead, place it on the child’s shoulder when shooting the x-ray to assess radiodensity.
PATIENT 4
A 65-year-old female with diabetes presents with odynophagia and neck pain after swallowing a fish bone 4 days prior. On exam, she has trismus and limited range of motion of the neck. She has no apparent respiratory distress and is handling her secretions, but she holds her neck in flexion and does not want to lie flat.
What would we expect to find on soft tissue neck radiograph?
This patient has a concerning story for retropharyngeal abscess. While CT neck with IV contrast can delineate phlegmon versus abscess and help with surgical planning, an x-ray is an appropriate first step if there is concern for airway compromise in the supine position.
Findings consistent with retropharyngeal abscess include: prevertebral swelling, reversal of normal cervical lordosis due to muscle spasm, air fluid levels, and gas.

Significant prevertebral swelling, gas noted at C3-C4, and loss or cervical lordosis.
* Case courtesy of Dr. Ian Bickle, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 30018
References
- Virk JS, Pang J, Okhovat S, Lingam RK, Singh A. Analysing lateral soft tissue neck radiographs. Emergency Radiology. 2012;19(3):255-260.
- Chawla A, Shenoy J, Lim TC, Singh D. Schematic interpretation of lateral neck radiographs of adults in the emergency department: a pictorial view. Emergency Radiology. 2016;23:79-87.
- Rose E. Pediatric Respiratory Emergencies: Upper Airway Obstruction and Infections. In Walls RM, ed. Rosen’s Emergency Medicine. Vol 2. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017; 2069-2080.
- Lee SH, Yun SJ, Kim DH, Jo HH, Ryu S. Do we need a change in ED diagnostic strategy for adult acute epiglottitis? Am J Emerg Med. 2017. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2017.04.039.
- Capps EF, Kinsella JJ, Gupta M, Bhatki AM, Opatowsky MJ. Emergency imaging assessment of acute, nontraumatic conditions of the head and neck. Radiographics. 2010;30(5):1335–1352.
Written by: Hannah R. Hughes, MD, MBA
Edited and posted by: Jeffrey Hill, MD, MEd





